Key Points:
COVID
- In today’s Recommendation for Industry, we discuss the globally increasing respiratory diseases, which we see as likely attributable to annual seasonal trends. Read more below.
- FDA, CDC greenlight updated COVID boosters for younger kids. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced that it has authorized for emergency use the updated bivalent (two-strain) COVID boosters for children as young as 5, and shortly after, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced its recommendation, which paves the way for the shots to be given. The Moderna booster is approved for kids as young as 6 years old, and the Pfizer version is now authorized for kids down to 5 years old. A few days ago in its weekly update, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) said COVID cases in kids for the week ending Oct 6 slightly increased from the previous week, with nearly 40,700 cases reported. Of the more than 2.8 million cases reported to the WHO, the five countries reporting the most were Germany, China, France, the United States, and Italy. Deaths stabilized last week, with about 9,000 fatalities reported. The drop was felt across all regions except for the Americas, which reported an 11% rise compared to the previous week. The global decline in COVID cases continued last week, with illnesses down 10% compared to the week before, the World Health Organization (WHO) said.
- A tangled web: 42% of Americans ignored COVID precautions or lied about taking them. During the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, 4 out of 10 Americans didn’t follow public health measures or lied about being compliant, mostly because they wanted life to feel normal and exercise their personal freedoms, reveals a survey published yesterday in JAMA Network Open. A total of 41.6% of respondents said they misrepresented or didn’t follow at least one public health measure, while 24.3% told someone they were with or about to be with that they were taking more COVID-19 precautions than they were, 22.5% broke quarantine rules, 21.5% avoided getting tested when they thought they might be infected, and 20.4% didn’t disclose suspected or confirmed infection when entering a doctor’s office. Roughly 60% of participants reported seeking advice from a doctor on COVID-19 prevention or treatment.
Food Safety & Public Health
- Researchers find monkeypox virus on hospital surfaces, in air. A new study from the United Kingdom shows widespread monkeypox DNA surface contamination in healthcare settings, with 93% of surfaces in occupied patient rooms contaminated, and significant contamination on healthcare worker personal protective equipment (PPE). The study, published in The Lancet Microbe, was based on testing completed on four respiratory isolation rooms in the Royal Free Hospital in London. Of 20 air samples taken, 5 (25%) were positive, including 3 of 4 air samples collected before and during a bedding change. In other monkeypox research news, a mobile app for Android phones is now able to use deep learning to offer a preliminary monkeypox diagnosis based on users’ pictures of rashes.
- Heart group urges families to eat meals together to lower stress. A new American Heart Association survey says 91% of parents notice their family is less stressed when they eat together. Such meal-sharing could be a simple way to help manage chronic stress that can increase a person’s lifetime risk of heart disease and stroke, the heart group says. Beyond stress relief, the national survey found that 67% of adults said sharing a meal reminds them of the importance of connecting with other people, and 54% said it reminds them to slow down and take a break. Nearly six in 10 survey respondents also said they are more likely to make healthier food choices when eating with other people, but they have trouble scheduling with their friends or family to share meals.
- FDA releases materials on safety of fish for National Seafood Month. October is National Seafood Month, and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration is releasing new educational materials on the food safety of fish. Infographics related to eating fish, along with educational resources can be found here.
- FDA and Federal Partners Launch Study on the Role of Seafood Consumption in Child Growth and Development. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced the launch of an independent study by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) on the Role of Seafood Consumption in Child Growth and Development. This study is designed to provide the most up-to-date understanding of the science of seafood consumption and child growth and development. Better understanding the science on mercury exposure from food is an important step in the cycle of continual improvement in the FDA’s Closer to Zero Action Plan.
- FDA tightens import restrictions on honey, seafood, and tamarind products. Click here to go to the FDA page with links to details on specific alerts.
- Retail Food Protection– The FDA launched the Retail Program Standards Reference System (RPSRS), a searchable knowledgebase of current Retail Program Standards interpretations. The searchable database can be found on Retail Program Standards landing page (Voluntary National Retail Food Regulatory Program Standards – August 2022. The database itself can also be accessed on Retail Program Standards Reference System (RPSRS).
Recommendations for Industry
Respiratory Disease Increase Likely Attributable to Annual Seasonal Factors
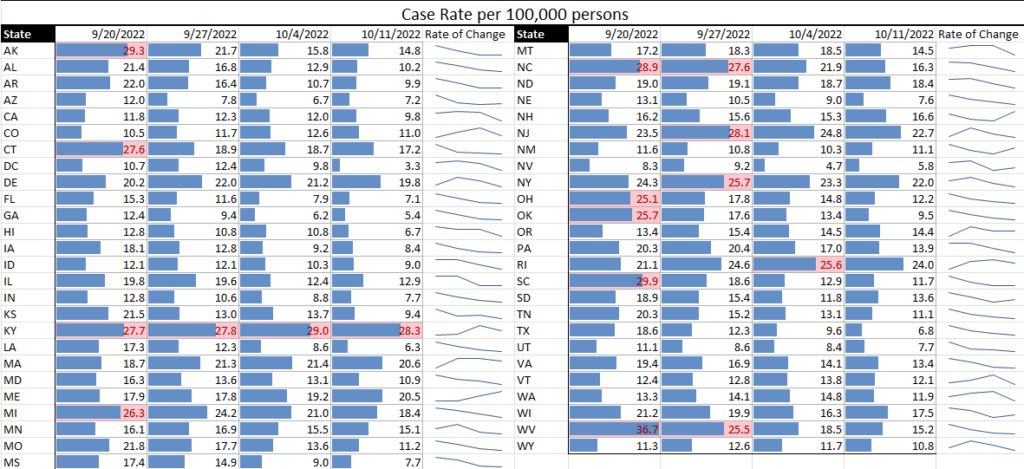
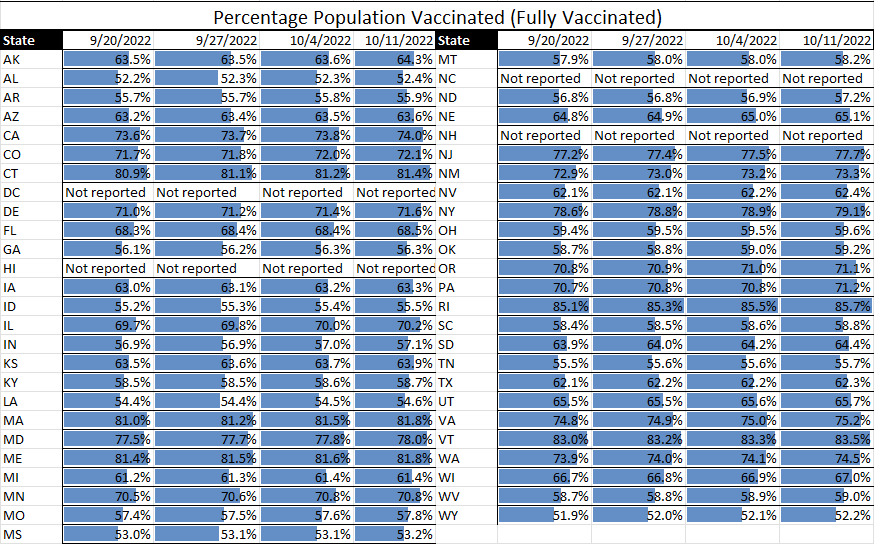
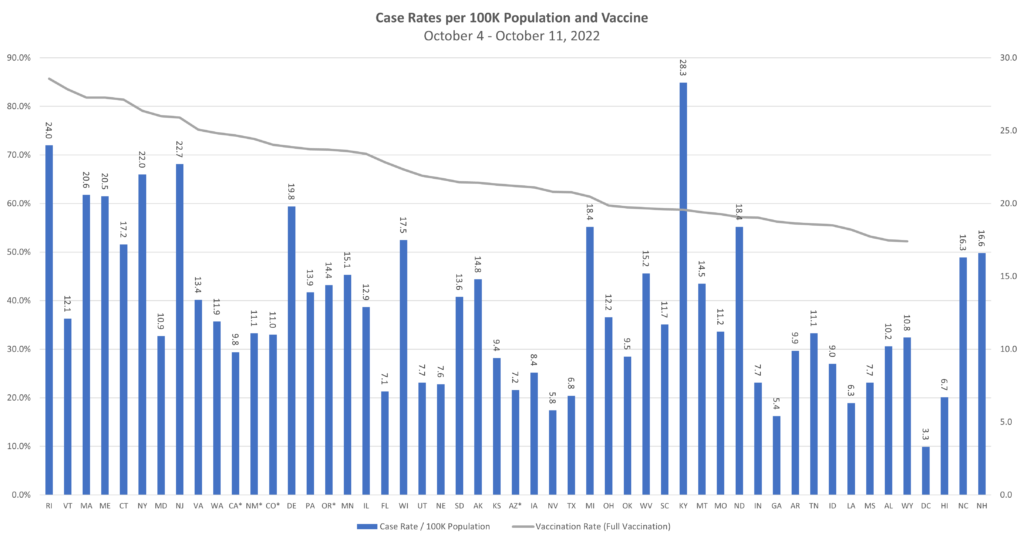
The trend of a rise and fall in communicable diseases is continuing this week, with TAG’s Communicable Disease Risk Matrix Analysis showing a continued decline in monkeypox, a distinct increase in influenza in some states, and a slight increase in COVID in the U.S. – but no states with high TPRs and case rates.
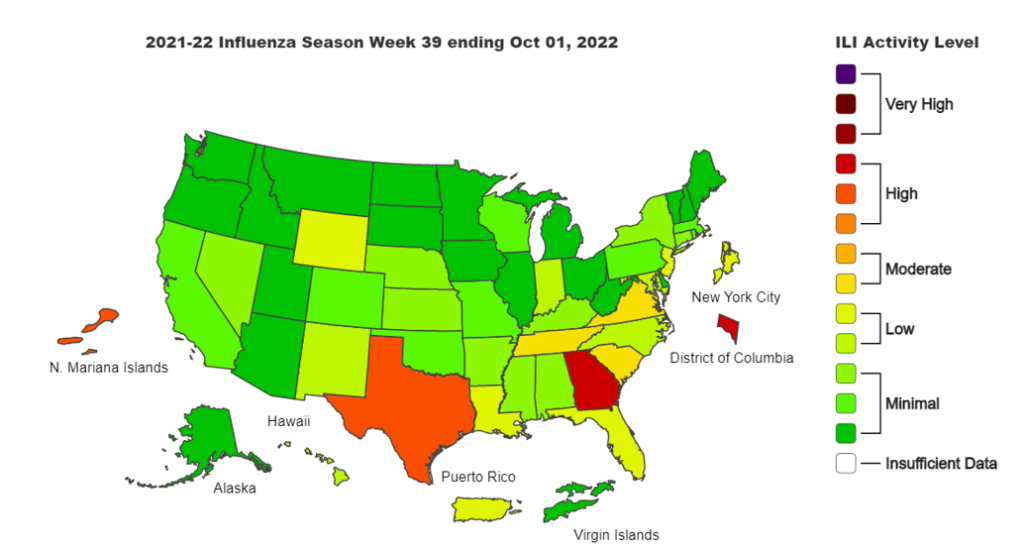
- Influenza cases are still low but are at higher levels than this time last year, particularly in southern states. Because of this, we would expect cases to increase at a faster rate as well. This increase is being seen both in the U.S. and globally.
- For COVID, although the U.S. remains at low levels, Europe is seeing a rise in cases, especially in those 65 and older. At this point, we would attribute the increases to the regular, anticipated fall increase in respiratory disease.
With both influenza and COVID being primarily upper respiratory diseases, it can be difficult to differentiate between the two without the person taking a COVID test. Because of this, we (yes, once again) caution businesses to keep your infectious disease protection policies in place, having workers stay home when ill.
COVID Risk Matrix:
Monkeypox:
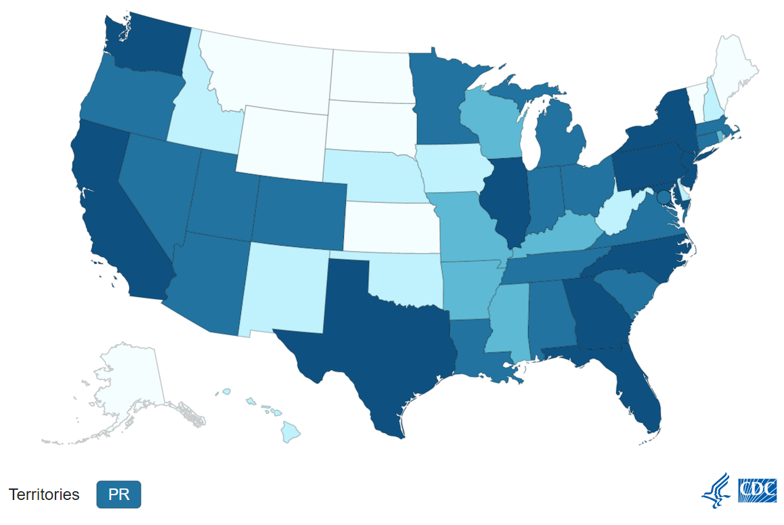

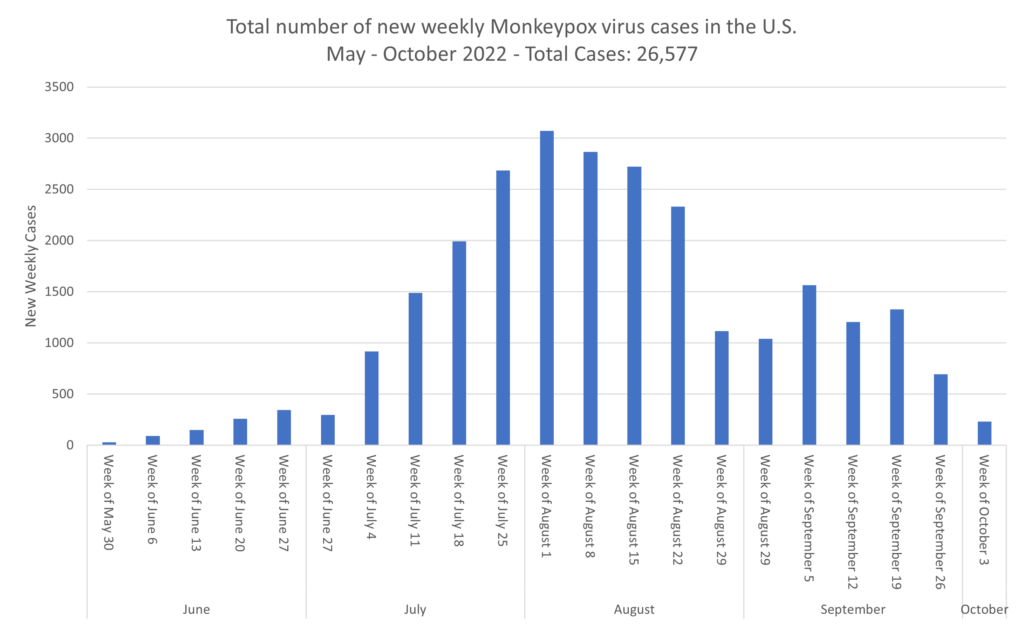
Influenza:
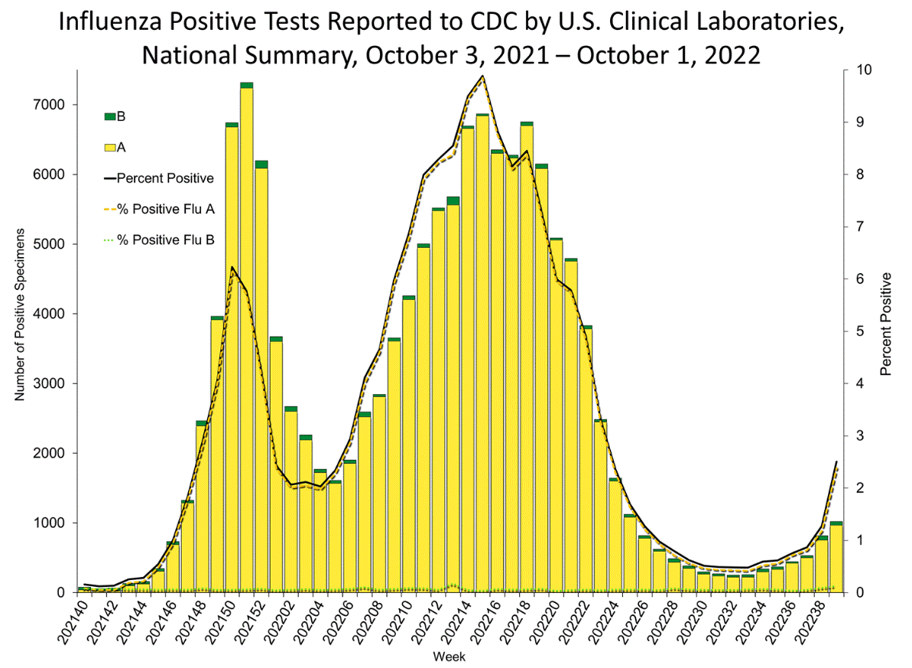
In case you missed it:
COVID
- In Tuesday’s Recommendation for Industry, we discussed the long-term impacts of infectious diseases. Read more here.
- Rising COVID levels in Europe especially affect seniors. COVID activity continued to rise in many European countries last week, up 14% compared to the previous week in people ages 65 and older, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) said today in a regular update. The pooled rate in Europe for all age-groups has been rising for the past 3 weeks, and the impact on seniors is leading to rising hospital indicators. Within the U.S., the BA.5 proportion dropped from 81.5% to 79.2% of sequenced samples. Meanwhile, the BF.7 subvariant rose from 3.3% to 4.6%, BA.2.72 rose from 1.5% to a share of 1.8%, and BA.4.6 rising slightly from 12.7% to 13.6%. Additionally in the U.S., the 7-day average for new daily cases was at 43,692, the CDC said yesterday, down from a 7-day average of 47,112 reported a week ago. Hospitalizations and deaths also continued downward trends. So far, 11.5 million people have received the updated COVID booster, up from 7.5 million the previous week.
- Omicron infection more effective than earlier variants against BA.4/BA.5 reinfection. Pre-Omicron infection at least 90 days before reinfection was 35.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 12.1% to 52.7%) effective against symptomatic BA.4/BA.5 reinfection and 27.7% (95% CI, 19.3% to 35.2%) effective against symptomatic or asymptomatic BA.4/BA.5 reinfection. Pre-Omicron infections occurred a median of 518 days before symptomatic BA.4/BA.5 infections, compared with a 189-day interval between the initial Omicron infection and the BA4/BA.5 reinfection—or a difference of 329 days. For any BA.4 or BA.5 reinfection, the difference was 309 days (490 vs 181). The study authors noted that BA.4 and BA.5 can escape neutralizing antibodies such as those conferred by previous infection or vaccination.
Food Safety & Public Health
- Monkeypox:
- Monkeypox study spotlights role of sexual transmission. A new study of GeoSentinel Network data involving 226 monkeypox cases from 15 countries shows that, of 219 patients for whom data were available, 216 (99%) reported sexual or close intimate contact in the 21 days before symptom onset. The Food and Drug Administration has issued an emergency use authorization for Abbott’s monkeypox test, which will offer real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test results for clinicians. The test relies on swabs of lesions. This is the first commercial test to be authorized for monkeypox detection. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on Oct 7 reported 172 more monkeypox cases, raising the national total to 26,557. The global total stands at more than 60,000 cases in 105 countries.
- Report: Monkeypox case rates 5 times higher in Black Americans. A new report from the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF) based on Centers for Disease Control (CDC) data reveals that monkeypox case rates in the US disproportionately affect Black and Latino Americans, with Black Americans having case rates 5 times of those found among White peers (14.4 cases vs. 2.6 per 100,000). In global news, the World Health Organization (WHO) published its seventh monkeypox situation report on the current outbreak, noting 25 total deaths worldwide this year due to the virus. Thirteen of the deaths are in Africa.
- Flu:
- The US CDC has said that “Seasonal flu activity is low at this time, but there are signs that activity is beginning to increase.” For example, NY is seeing cases at 4x now than where they were at this time last year and Boston is reporting that pediatric cases of the flu are rising.
- According to the EU health authority ECDC, the most recent outbreak of bird flu is the worst such epidemic ever recorded in Europe. Nearly 2,500 outbreaks were detected in poultry farms during the 2021-2022 bird flu season, according to a report by the agency released on Monday. 48 million animals were killed.
- Norovirus:
- Health risks in the Žalec, Slovenia water supply system continue after some 100 locals sought medical help due to digestive issues earlier this week. Norovirus was detected in the water system.
- Pertussis (whooping cough):
- The FDA announced it approved a vaccine administered during the third trimester of pregnancy to prevent pertussis — whooping cough — in infants younger than 2 months of age. When the vaccine (Boostrix, GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals) is administered, it boosts antibodies in the pregnant mother, which are transferred to the developing baby, according to a press release from the FDA. Infants younger than 2 months of age are too young to be protected by the childhood pertussis vaccine series. This is the first vaccine approved specifically for use during pregnancy to prevent a disease in young infants whose mothers are vaccinated during pregnancy.
- Tips for tailgaters looking to avoid food poisoning this football season. Penn State Extension food safety experts have compiled pointers for those planning to tailgate this season and are offering tailgaters a free brochure of food safety tailgating tips that can be downloaded here.
- New E. coli outbreak traced to frozen falafel sold at Aldi stores. The FDA has reported 20 people infected with five requiring hospitalizations in relation to the E. coli outbreak related to falafel from Aldi’s. The sick individuals are located in Florida, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Ohio, and Wisconsin. The affected products were sent to 36 states and individuals are advised to throw away this product if you have not yet consumed it.
- Cider recalled in Quebec because of lead contamination. Le Verger à Ti-Paul Inc. of Saint-Elzéar, Quebec, Canada, is recalling their company’s brand of Cider because of lead contamination. Consumers and retailers should not use, sell, serve, or distribute the affected products.
- Gaton’s Foods Dairy expands recall of cheeses sold in Canada over Listeria concerns. Gaton’s Foods Dairy has expanded its recall of certain Nature’s Best and Zavat Chalavfrom brand cheeses from the marketplace because of possible Listeria monocytogenes contamination. For the complete list of currently recalled cheeses, click here.