We are continuing to see an upward trend in norovirus outbreaks, as is reported by CDC on a monthly basis. While the trend is tracking fairly consistently with that of 2022, there is a higher number of outbreaks than in the last few years, though we are still much lower than the peak trend. As such, we expect numbers to continue to increase, with cases likely to peak in February and March – if we continue to follow previous trends.
Norovirus is a very contagious virus that causes vomiting and diarrhea and impacts people of all ages. With infected persons able to shed billions of virus particles, and only a few particles needed to make others sick, norovirus can spread quickly.
Norovirus is the #1 cause of foodborne illness, but it is not always associated with food. It can be passed through
- Direct contact with an infected person.
- Consumption of contaminated food or water.
- Touching of contaminated surfaces and then putting unwashed hands in your mouth.
The virus is persistent and requires aggressive techniques to be inactivated including identifying and excluding employees who are ill, having policies to incentivize ill employees to stay home; responding quickly to contain and disinfect any bodily fluid spills and surrounding areas and excluding others from the area if an employee or customer becomes ill, using proper sanitation chemicals (e.g., disinfectants) with claims against norovirus for cleaning according to the labeled instructions.
For more information on norovirus, download TAG’s Norovirus Disease Fact Sheet.
COVID Risk Matrix:
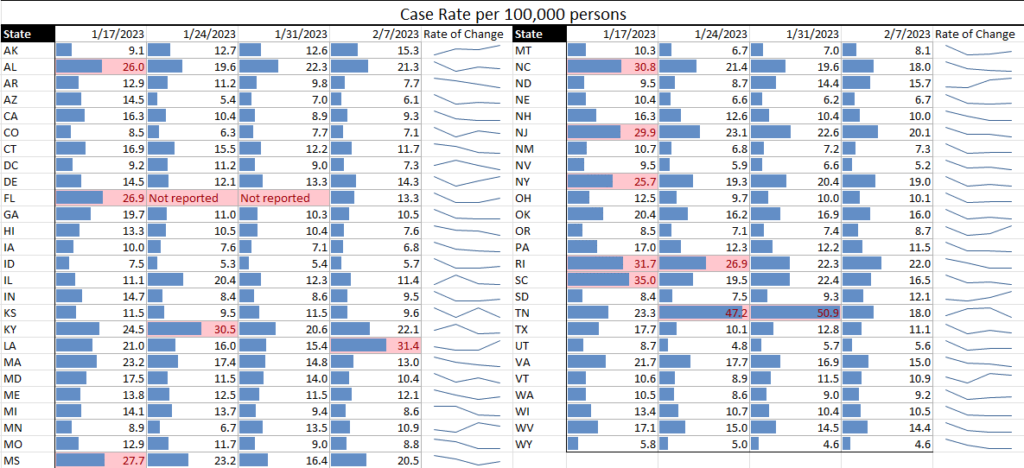
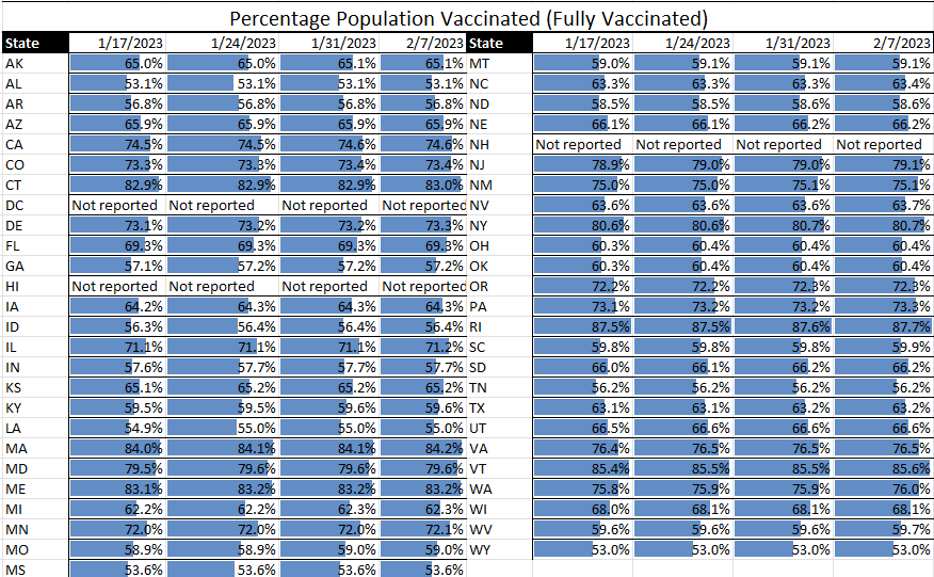
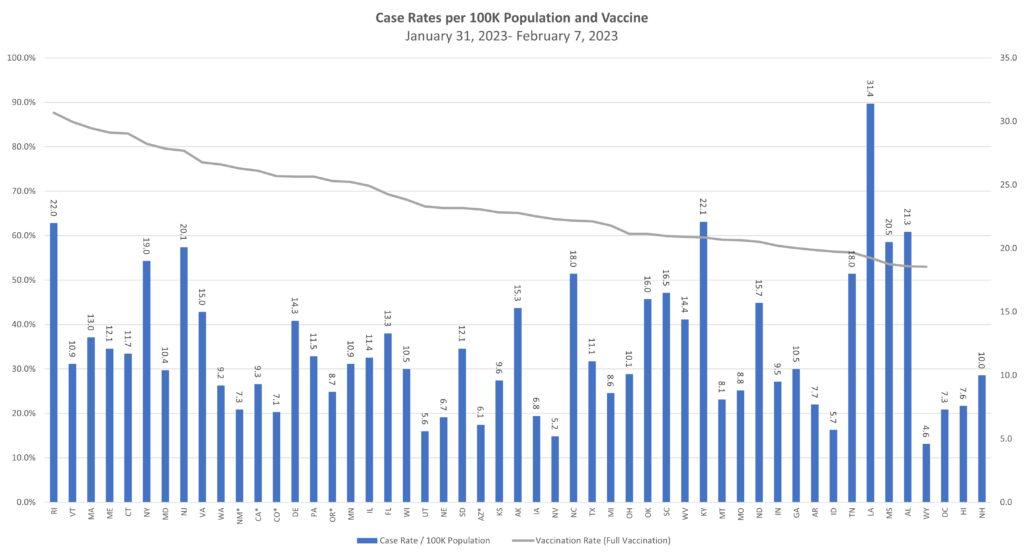
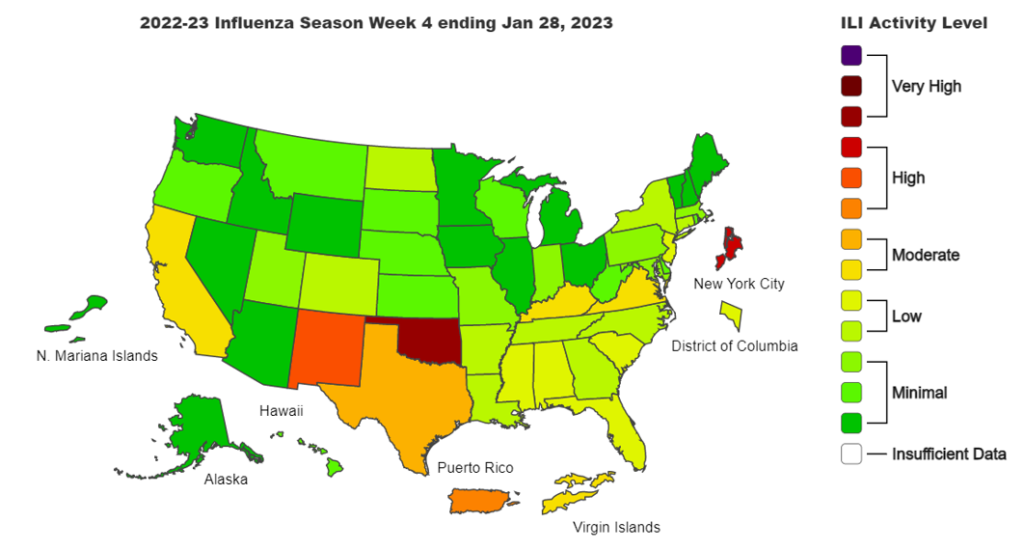
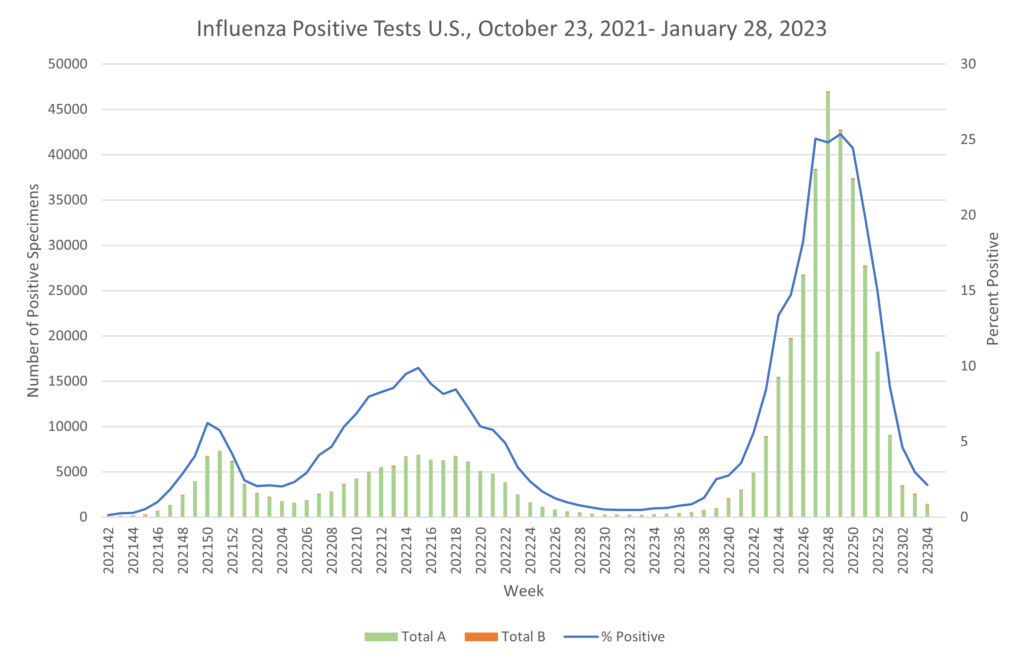
Influenza:
Infectious Disease News
- Chicken pox cases are rising in India. 2000 cases occurred in the past year and there were 9 deaths in January 2023.
- Measles cases are rising in Russia, more likely due to associations with travel than with low vaccination rates.
- Research from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic revealed that there needs to be a focus on the development of a vaccine aimed at RSV.
- Studies, which appeared in The Lancet Infectious Diseases, describe an outbreak of different strains of multidrug-resistant (MDR) Shigella in Washington state and the emergence of an extensively drug-resistant (XDR) strain in England. Both studies suggest that drug-resistant Shigella presents a growing public health challenge that demands a coordinated response.
- COVID and flu markers continue downward trends. XBB.1.5 proportions continue to rise in all regions. Flu has continued to have a steady decline in cases, of which 99.4% have been Influenza A.
- US public health emergency for mpox expired as it was slated to end on January 31, but a renewal wasn’t declared due to few cases. The total as of Jan 25 stands at 30,093 cases, 26 of them fatal.