While the global nature of the food industry has great benefits, it also causes a number of challenges, in this case, the transmission of infectious disease. As of June 8, 2023, there were 16 confirmed U.S. cases of measles (rubeola) across 11 jurisdictions, with 14 (88%) linked to international travel.
Because of the extreme contagion of measles, with one infected person able to infect 90% of their unvaccinated close contacts, CDC has issued guidance urging travelers to ensure they are vaccinated against measles before summer travel. With 88% of U.S. cases linked to international travel, those travelers are particularly at risk.
The CDC recommendation for measles is a first dose at 12 to 15 months of age, and a second dose at 4 to 6 years. Additionally, students at post-high school educational institutions who do not have presumptive evidence of immunity (documentation of vaccination or having had measles, or birth before 1957) need two doses of MMR vaccine, separated by at least 28 days. Adults without presumptive evidence of immunity should get at least one dose; those who are traveling internationally or will be in a setting with a high risk of measles should ensure they’ve had two doses separated by at least 28 days.
Recent declines in routine measles vaccinations due to the COVID-19 pandemic has reduced U.S. vaccination rates close to 92%. Measles elimination hinges on vaccination coverage remaining above 95% to retain sufficient community protection. Because of this, as many as 9 million children in the U.S. are estimated to be susceptible to measles.
Thus, businesses can be impacted on two fronts from the rise in measles:
- International travelers bringing back the disease.
- Parents having to stay home with ill children who contract measles.
TAG’s advice is to communicate these facts with your employees, ensuring they understand the issue and urging those who are not to be vaccinated. You may also want to post TAG’s Measles Fact Sheet on a board to provide workers with the facts.
COVID Risk Matrix:
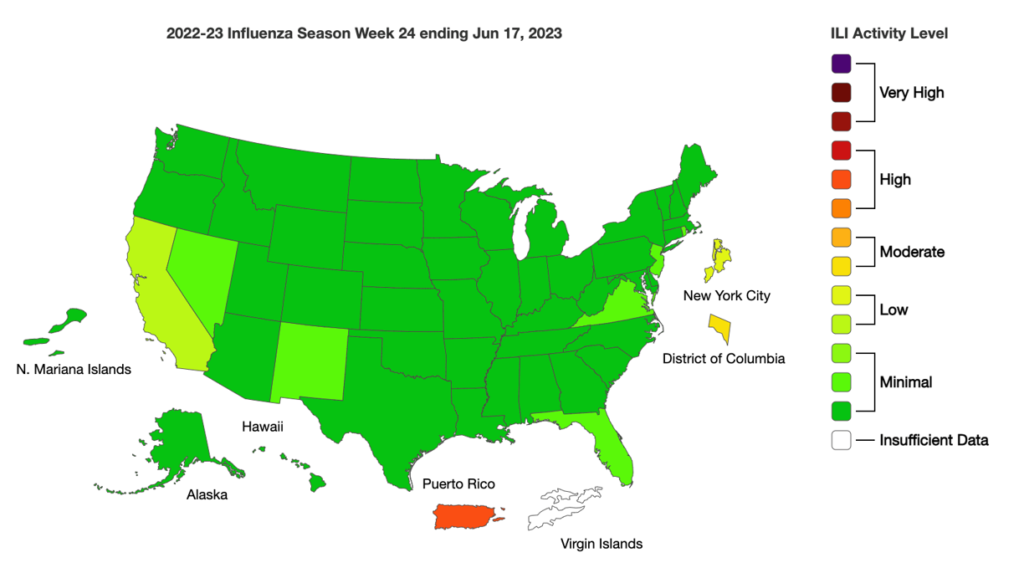
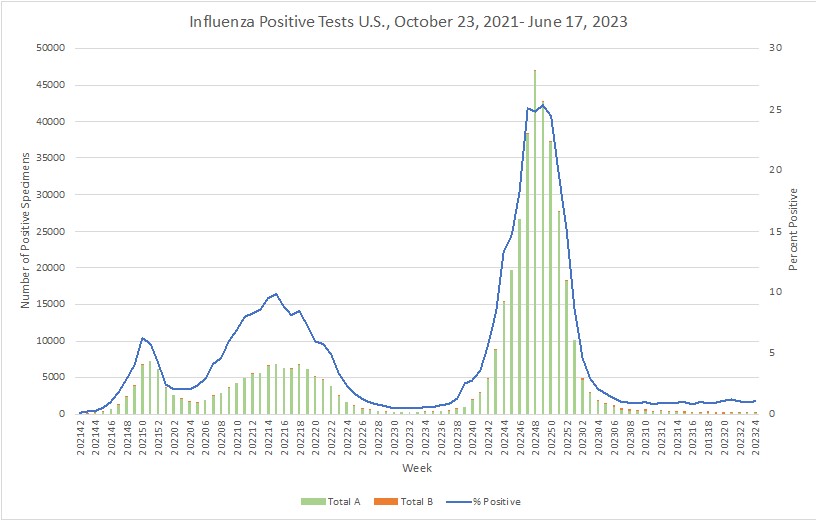
Influenza:
Infectious Disease News:
- With the annual monsoons starting in India, infectious diseases including dengue, flu and rat fever are rising. Disease can be transmitted by mosquitoes, infected foods, or from person to person spread.
- The CDC is urging people to ensure they are vaccinated against measles before summer travel. International travelers are particularly at risk, the CDC said, noting that 88% of all cases in the U.S. so far this year are linked to international travel.
- There are two reports of possible zoonotic transmission of TB from animals to humans:
- 12 blackbuck deer from Jamshedpur Zoo in India tested TB positive in Bengal Safari Park. 4 workers have also tested positive.
-
- Michigan state officials have confirmed that cases of tuberculosis were found in February in monkeys imported from overseas. The primates had undergone a 31-day Centers for Disease Control and Prevention mandated quarantine at a facility in Florida before arriving in Michigan. The CDC quarantine apparently failed to detect infections in any of them. Two workers have tested positive, although it’s not confirmed if their illnesses came from the infected animals.
- Note – Zoonotic transmission is responsible for about 2% of TB cases in the US. Cattle are the most important animal reservoir for M. bovis (the causative agent of TB) in relation to zoonotic exposure of humans, but the disease can affect many other animals as well.
- The Texas Department of Health and Human Services (TDHHS) has reported its first case of malaria since 1994, which follows four cases in Florida.