A newly released report from the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Emerging Risk Knowledge Networks (EREN) has identified eight food safety issues as emerging risks. The group discussed 18 potential emerging issues, with each presented in the form of a standard briefing note, given a unique ID number and classified as a new consumer trend or as microbiological, chemical, both, or other. Following is further information on some of those that TAG sees as being of key interest:
- Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia albertii (STEA). Although it was first described in 2003, this STEC pathogen has been little known and often identified as E. coli due to its poorly defined biochemical characteristics and general obscurity and its resemblance to E. coli in its phenotypic characteristics. Several studies examined the environmental prevalence, detection possibilities, genomes and pathogenicity potential of STEA strains. STEA has been isolated from various animals, such as pigs, cats, and birds, but the natural reservoir of E. albertii is still unclear; this information would be essential to determine transmission dynamics and prevent E. albertii infections. As such, the recommendation is for the network to collect data on incidence, prevalence in humans and risk exposure pathways to better characterize the hazard.
- Health risks of coconut oil. Along with consumer trends toward healthier nutrition has come an increasing use of coconut oil. Most oils found in our regular diet contain mainly long-chain fatty acids (LCFA), coconut oil contains mainly medium-length fatty acids (MCFA) which have become increasingly important in nutrition. While there has been some evidence to suggest that MCFAs do have some health benefits, there have also been signs pointing toward some health risks. The EREN recommendation is for further research to strengthen the evidence basis on potential toxicity and check national data to see if an increasing trend in food consumption of coconut oil could be confirmed.
- Decreased use of pesticides and fertilizers. While we often see pesticides and fertilizers disparaged for their danger, EFSA focuses on how the reduction in the use of chemical pesticides to combat pests may increase them. Pests such as broad ban beetle or the cabbage-stem flea beetlecan have important consequences on the production of broad bean and rapeseed, respectively. Both broad bean and rapeseed provide nutritional and health benefits, and without them the human diet would be losing the beneficial vitamins and minerals they provide. Additionally, there are cases where the quality and safety of food products could be compromised by the increased presence of pathogens and spoilage organisms on edible plants. Farm-to-fork aspirational targets should parallel development of effective new tools to diminish the rise of potential emerging issues; following implementation, plant health, food safety and security, human health, as well as the environment should be taken into consideration.
- Overdosing of Vit D in Food Supplements. Several cases of severe hypercalcaemia requiring hospitalization have occurred in previously healthy infants who were exposed to vitamin D supplementation in the form of food supplements. In 2019 and 2020, Poison Control Centers were called for at least 23 overdoses after consumption of a vitamin D-containing food supplement for children. With health professionals recommending substituting vitamin D-based medicines with vitamin D-enriched food supplements because of the preservatives or essential oils that these medicines may contain, some parents have substituted a “vegan” food supplement without paying attention to the dosage, which may be much higher. There is a risk for children because the concentration of vitamin D per drop can be very high, and there may be no recommended dose for different ages. There are many products with different concentrations/dosages, sometimes within the same brand, causing confusion, and other vitamins may be present in the food supplement for which there are no recommended daily doses for children. The Emerging Risks Exchange Network (EREN) stated that additional research is needed on the possible effect of Vit D chronic toxicity due to chronic low overdosage.
Other emerging issues included brevetoxins in French shellfish, new ovine pestivirus closely related to classical swine fever virus identified in Italy; a first detection of West Caucasian Lyssavirus in a cat in Italy; and the increasing importance and/or awareness of Mycoplasma bovis infections in Belgium.
The full report is available at EFSA.
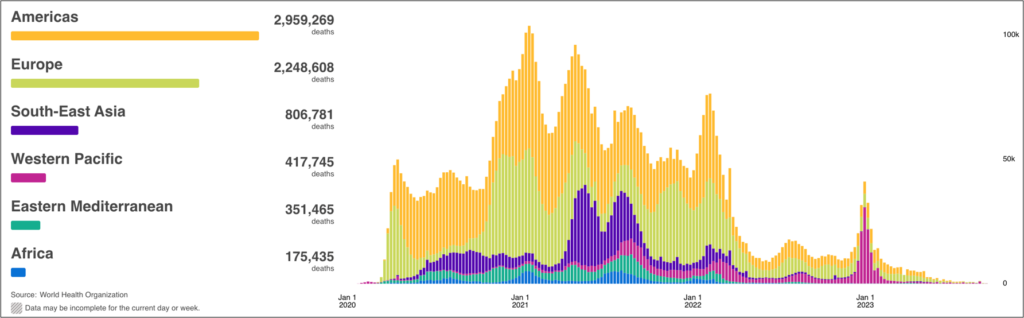
COVID Risk Matrix:
Influenza:
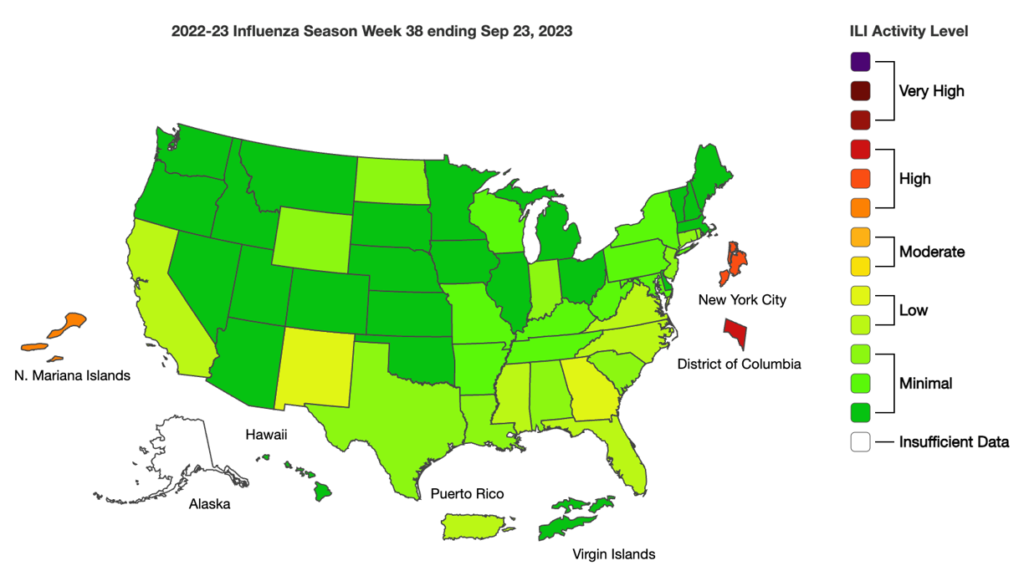
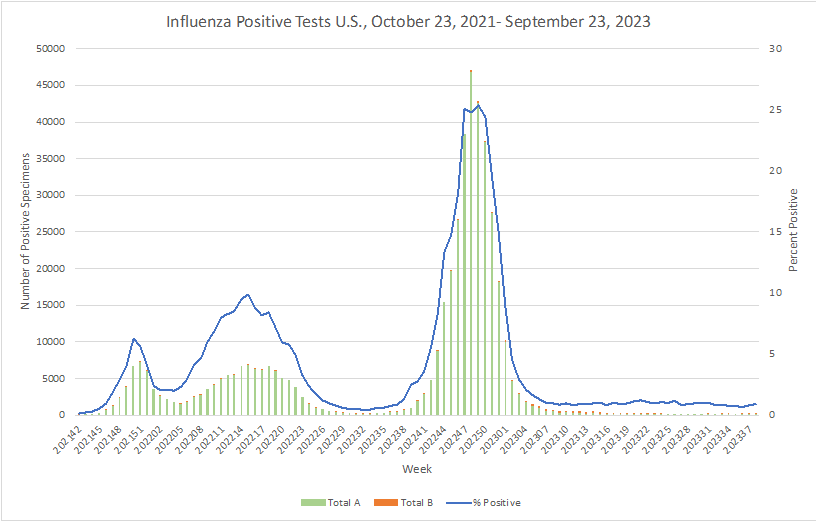
- The CDC has published similarities and differences that can be noted between the flu and COVID-19. From data so far, we know COVID-19 spreads more easily than flu and can cause more severe illness in some individuals. Since the differences cannot be easily identified between the two illnesses when just looking at signs and symptoms, getting tested is important. To prevent illnesses, the CDC recommends getting vaccinated for both.
- Officials in the UK are worried about possible outbreaks of measles, polio, and diphtheria, due to under vaccination. It has been reported only 74% of children have received the second dose of the Measles Mumps and Rubella vaccine (MMR) by the age of five.
- The World Health Organization says Tuberculosis is still one of the world’s top infectious killers. It says annually more than 10 million people fall sick with TB and over 1 million die. Drug resistant TB continues to be a major contributor to antimicrobial resistance with close to half a million people developing drug-resistant TB every year.
- In Denmark, 200 cases of whooping cough were detected during the week beginning September 11th, ten times over the normal level, the national infectious disease agency State Serum Institute (SSI) said in a press statement on Thursday. The month of August saw 439 confirmed cases, which is four times the regular level.
- Health officials have provided an update on the Calgary E. coli outbreak saying that meatloaf and veganloaf meals prepared in the shared kitchen was most likely the source of the outbreak.
- Health Canada has approved Pzifer’s updated COVID vaccine to protect individuals 6 months of age and older. Moderna’s updated vaccine was approved in early September.





