The COVID of 2024 is not the same as the COVID of 2020. SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is constantly changing and its genetic code is mutating with new variants expected to continue to emerge.
Because of this, circulating variants of the virus are continually reassessed and vaccines reformulated to target the current variants. The variants are identified through the collection and sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 specimens from CDC’s national genomic surveillance system, CDC-contracted laboratories, and state or local public health laboratories. The proportions of SARS-CoV-2 variants in a population are then calculated nationally, by HHS region, and by jurisdiction.
From all this, for the 2024-2025 season, Moderna and Pfizer have developed updated mRNA COVID-19 vaccines which include a monovalent component that corresponds to the Omicron variant KP.2 strain of SARS-CoV-2. The vaccines, which have been approved and granted emergency use authorization (EUA) by FDA, involve a one- or two-dose series related to age and condition of each person and are available for individuals 6 months and older. Contact medical providers for more details. The vaccines closely target the currently circulating variants and provide better protection against serious consequences of COVID-19, including hospitalization and death.
With COVID cases currently trending upward in more than half the states of the U.S., the government will also be offering free COVID-19 tests again. Available at the end of September, U.S. households can order four free COVID-19 tests at COVIDTests.gov. The tests will detect current COVID-19 variants and can be used through the end of the year.
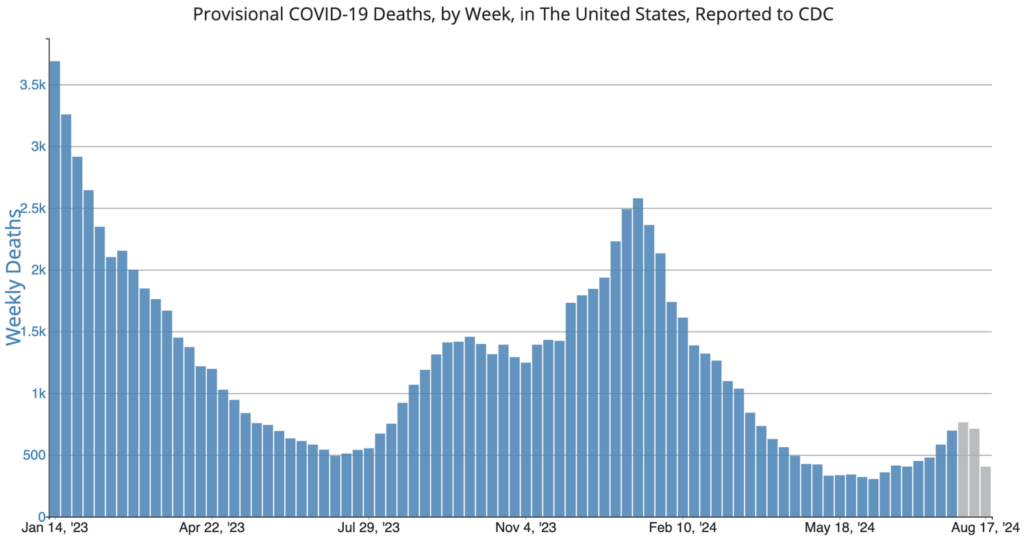
COVID Risk Matrix:
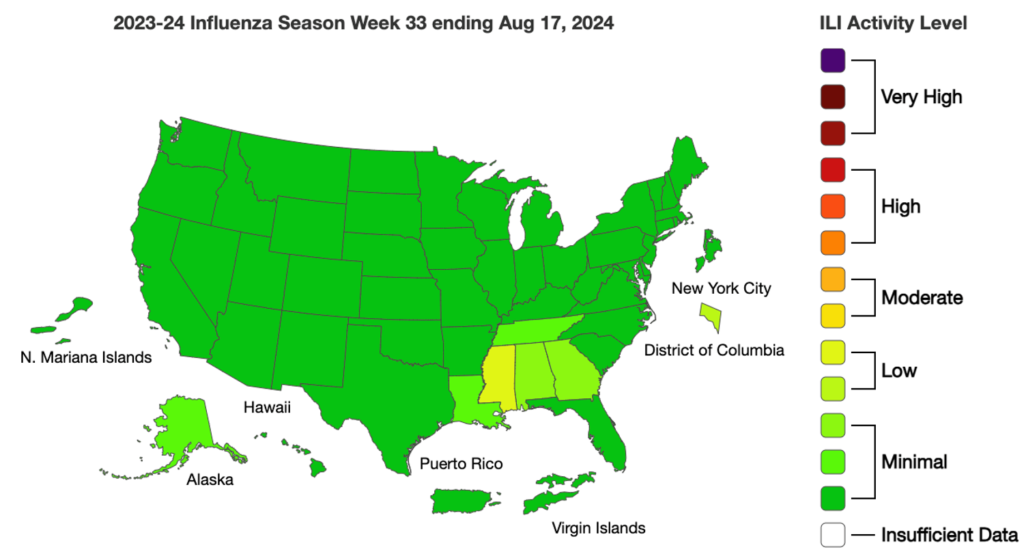
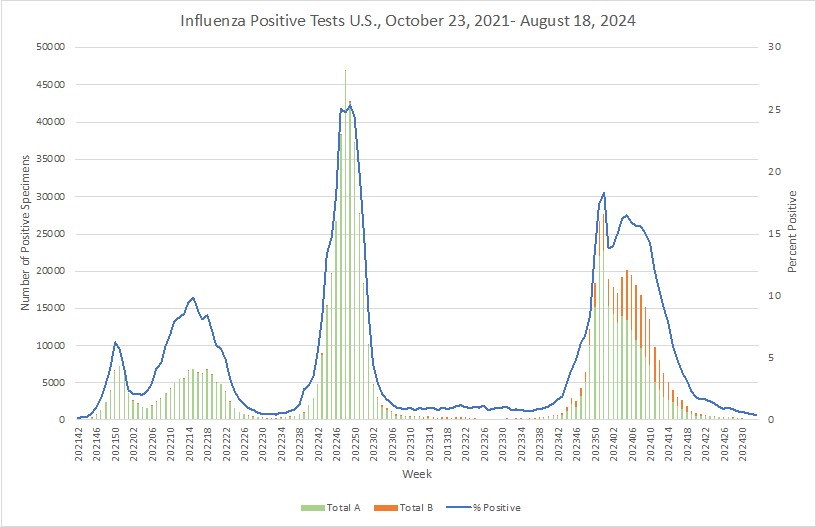
Influenza:
- Over 21% of tests are positive for COVID in Quebec, Canada. Some hospitals in the area (Laval) are now re-introducing masking across facilities in response to the uptick in cases among employees and the city’s population as a whole.
- A whooping cough outbreak has been declared across New Brunswick, Canada. 141 cases have been reported.
- The FDA approved and authorized the emergency use of the updated mRNA COVID-19 vaccines to better protect against the currently circulating variants. The vaccine corresponds to the KP.2 strain for individuals 6 months and older. The vaccines should be available very soon and may involve 1 or 2 dose series related to age and condition.
- On August 22, the FDA granted emergency use authorization for two new combined COVID-19 and influenza tests. The Nano-Check Influenza-COVID-19 Dual Test is authorized for use by laboratories to detect and differentiate influenza A and B and SARS-CoV-2 in nasal swab specimens. The Flowflex Plus COVID-19 and Flu A/B Home Test is authorized for home use for people aged two and older.
- An outbreak of Legionnaires’ disease has been reported in the metropolitan area of Milan. At least 4 people have died and 12 are hospitalized. The source has not been identified.
- The outbreak of Legionnaire’s disease in New Hampshire has now been expanded to seven cases. The source was identified as a cooling tower, and it has been cleaned and disinfected.
- A lack of awareness of the spread of tuberculosis may be an important factor contributing to the current burden of disease in India. Being aged 15-19 and living in rural areas are risk factors. Being unmarried is a protective factor for women, but not for men.
- There have been 49 recorded cases of tuberculosis in Kansas since the start of the year. Last year there were 46 total cases in all of Kansas last year. The reason for the large increase is not known.