As we experience less severe winters and increasing air temperatures, the risk and range of tick-borne illnesses grow. Historically, very cold, dry winters are poor conditions for tick survival, and recent winters have been anything but. Over the last decade, Lyme disease cases have increased by 1,000% in Canada.
Ticks, parasitic arachnids ranging vastly in size, can carry infectious agents that pose serious health risks. Although not all ticks are carriers, bites from those that are, can expose humans to a variety of concerning symptoms and health conditions. Ticks, while found year-round, are most active in warmer months. Climate change has allowed for longer warm seasons up north and increasing habitats for ticks, as well as for host animals, such as deer, mice, and raccoons.
More favorable conditions over a wider range of locations have led to great population growth and longevity in ticks. In the first five months of 2024, 1,124 black-legged tick sightings have been reported in Ontario. In comparison, only about 120 ticks were sighted in the same amount of time five years ago. In Canada, a map of established risk areas in 2024 show black-legged ticks now occupy more urban and residential areas, increasing human risk for exposure.
Lyme disease, the most common tick-borne disease, is transmitted through a black-legged tick carrying Borrelia burgdorferi. This species is extremely small, making it difficult to spot. In the early stages of Lyme disease, one sign can be a “bull’s eye rash” around the site of the tick bite. However, this rash is not always experienced or witnessed, and a diagnosis may not occur until later stages of infection. Even if Lyme is suspected, some people experience pain for years without a diagnosis, as testing is unreliable, and symptoms vary. If left without diagnosis and treatment, Lyme disease can negatively affect the heart, joints, and nervous system. A wide range of other serious, painful, and even debilitating symptoms can occur, including fatigue, fever, dizziness, headaches, and memory loss. In rare cases, it can lead to death.
Another serious condition that can arise after a tick bite is Alpha-gal Syndrome (AGS), an allergy to alpha-gal, a sugar found in mammalian tissue and meat. The tick primarily associated with AGS is the lone star tick. Eating beef, pork, lamb, or other animal products can cause the allergic reaction in individuals with AGS. Symptoms include a rash, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, difficulty breathing, and—in some cases—an anaphylactic reaction.
As peak tick season is arriving, TAG recommends following preventive measures against tick bites, such as wearing long pants and closed-toe shoes, applying bug repellent, watching where you are walking, and checking for ticks when you return indoors. For more information on tick-borne infectious diseases and prevention, check out TAG’s fact sheet and contact us with any questions.
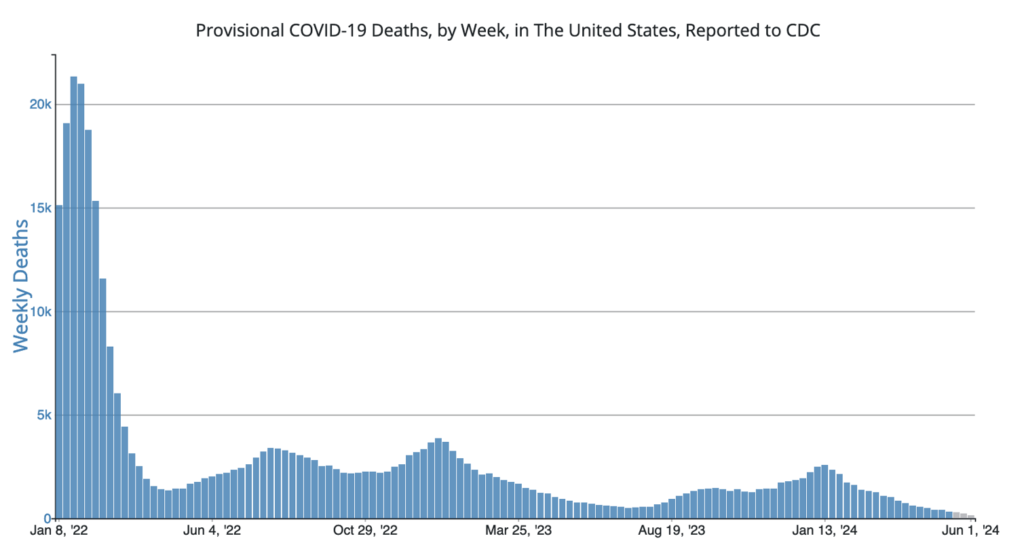
COVID Risk Matrix:
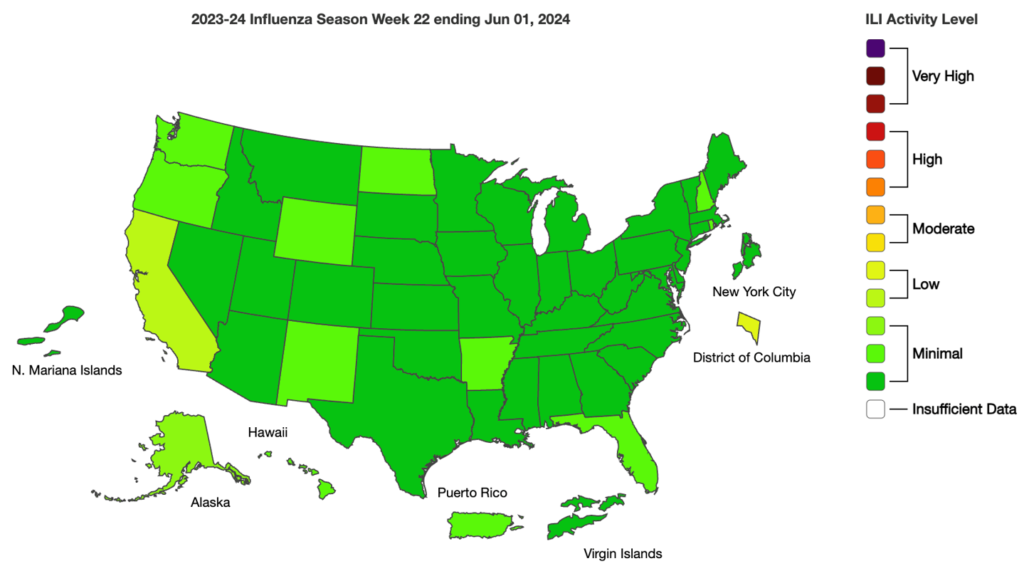
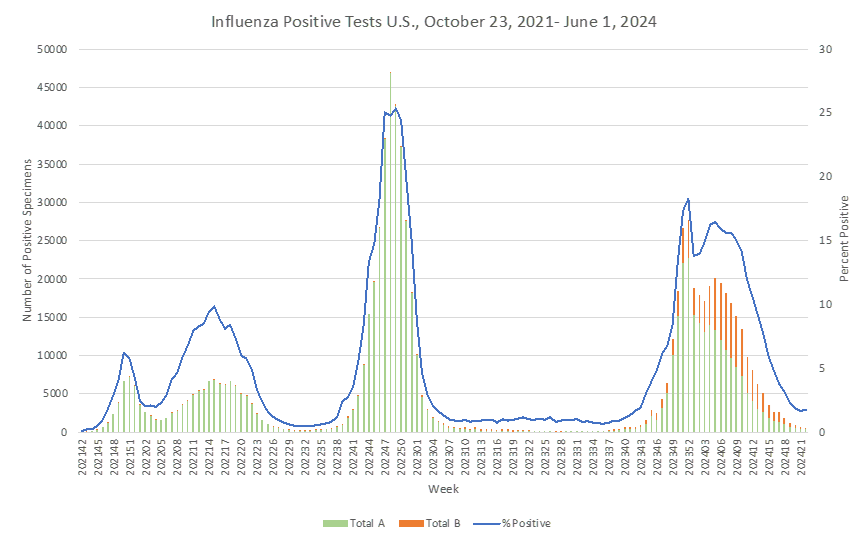
Influenza:
- The World Health Organization reported the first laboratory-confirmed human case of infection with A(H5N2) avian influenza in Mexico. However, the man who contracted bird flu in Mexico died due to chronic diseases and not the virus, Mexico’s health ministry said a few days later.
- Health officials in NYC report on the value of vaccination against chicken pox to help impact illness rates, especially among arrivals from countries that do not routinely give this vaccine. A recent CDC report stated that over 40% of cases were linked to exposures in a shelter or residential facility.
- Watmind USA has been granted Emergency Use Authorization by the US FDA for its over-the-counter lateral flow SpeedySwab Covid + FLU A&B Self-Test.
- Measles:
- In India, annual measles incidence per million has been increasing for the last three years, leading to the outbreaks across the province since the start of 2024. A large number of cases are reported in infants too young to receive their first dose of the vaccine.
- An outbreak of measles that originated in a Chicago migrant shelter and spread to four counties has been contained, according to the Illinois Department of Public Health. A total of 67 cases were reported, and no new cases have been reported in 42 days, which is two full incubation periods for the disease.
- Meningitis cases in Toronto are occurring at a rate double the typical average. To date, 13 have been reported. Vaccination is urged.
- So far in 2024 in St. Lucia, over 700 cases of gastroenteritis have been recorded, a 30% increase in the numbers recorded for last year at this time. A direct cause has not been determined.
- Whooping cough:
- The US CDC reports that cases of whooping cough are rising significantly across the United States. There have been almost 5,000 reported cases this year, which is nearly three times higher than this time last year.
-
- Rates of whooping cough are also up in France. For the first five months of 2024, 5,854 cases have been diagnosed, compared to 495 over the whole of 2023.
- China’s whooping cough epidemic got dramatically worse in April, with over 90,000 cases reported that month, an increase of over 80 times from the same month in 2023 and a threefold increase from the month before, official data showed.
- The FDA announced that it has advised the manufacturers of the licensed and authorized COVID-19 vaccines that the vaccines (2024-2025 Formula) for use in the United States should be monovalent (single strain) JN.1 vaccines to more closely match the currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 viruses.
- The CDC has released their strategy for enhanced summer 2024 influenza surveillance, in light of the continuing multistate outbreak of avian influenza A(H5N1) in dairy cows, poultry and other animals. They are focusing on enhanced surveillance to guide where additional risk management strategies are needed.